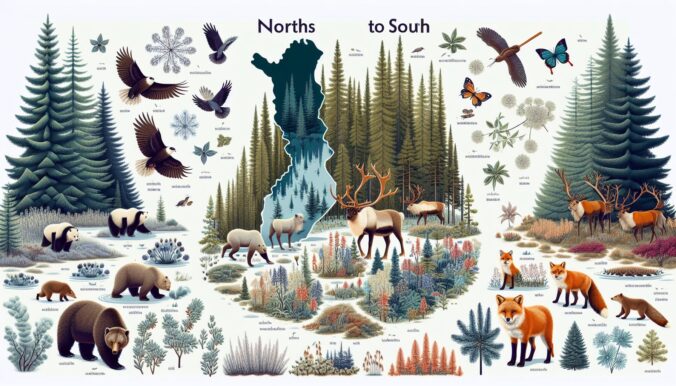
From its lush green forests to its stunning lakes and diverse wildlife, Finland is a country rich in biological diversity. This Nordic nation is home to a wide range of habitats, plants, and animals that contribute to its unique ecosystems. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of biological diversity in Finland and the importance of conserving these natural treasures.
Habitats and Ecosystems
Finland is known for its pristine nature, with nearly three-quarters of the country covered in forests. These forests are home to a diverse array of plant and animal species, including pine trees, spruces, and birches, as well as moose, bears, and wolves. In addition to forests, Finland also boasts thousands of lakes, rivers, and wetlands that provide habitats for countless aquatic species, such as fish, birds, and insects.
The country’s coastal areas are another important ecosystem, supporting a variety of marine life, including seals, seabirds, and fish. The archipelago off the southwest coast of Finland is particularly well-known for its biodiversity, with hundreds of islands teeming with life.
Plant Life
Finland is home to a wide range of plant species, from boreal forests to alpine meadows. Some of the iconic plants found in Finland include the cloudberry, the national berry of the country, and the saffron-colored marsh marigold. In the northernmost parts of Finland, where the climate is harsher, hardy plants like Arctic bearberry and mosses thrive.
Wildlife
The wildlife in Finland is diverse and abundant, with many iconic species calling the country home. Some of the most famous inhabitants of Finland’s forests include brown bears, reindeer, and lynx. Birdwatchers will also be delighted by the hundreds of bird species that can be spotted in Finland, including the majestic white-tailed eagle and the elusive Siberian jay.
Conservation Efforts
Despite its rich biodiversity, Finland faces threats from human activities such as deforestation, pollution, and climate change. To protect its natural heritage, the Finnish government has implemented various conservation efforts, such as designating national parks and nature reserves. These protected areas help to preserve the country’s unique habitats and species for future generations to enjoy.
In addition to government-led initiatives, many non-profit organizations and community groups in Finland are also working to conserve the country’s biodiversity. Through education, advocacy, and conservation projects, these groups are helping to raise awareness about the importance of protecting Finland’s natural environment.
Conclusion
Finland is a country blessed with an incredible array of habitats, plants, and animals that contribute to its rich biological diversity. From its ancient forests to its crystal-clear lakes, Finland’s natural beauty is a source of pride for its people and a treasure for the world to cherish. By recognizing the value of biodiversity and taking steps to protect it, we can ensure that Finland’s natural heritage continues to thrive for generations to come.